| [1]Lange R, Lüthen F, Beck U,et al. Cell-extracellular matrix interaction and physico-chemical characteristics of titanium surfaces depend on the roughness of the material. Biomol Eng.2002;19(2-6):255-261.[2]杨玉生,孙俊英,朱伟,等.松质骨源性人成骨细胞的分离培养和细胞密度效应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(3): 431-434.[3]雷荣昌,翦新春.松质骨支架与成骨细胞生物相容性的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2005,21(5):531-533.[4]章庆国,赵士芳,郭宗科,等.纳米相陶瓷支架与人成骨细胞生物相容性的体外实验研究[J].东南大学学报,2004,34(2):219-213.[5]余科,贾颖,刘敏,等.国产纳米级羟基磷灰石复合胶原膜降解产物的生物相容性研究[J].海南医学,2008,19(9):50-51.[6]史光和,黄晓斌,陈钢,等.人成骨细胞与异体脱钙松质骨成骨作用的实验研究[J].中国基层医药,2006,13(8):1254-1255.[7]Leong KF,Cheah CM,Chua CK.Solid freeform fabrication of three-dimensional scaffolds for engineering replacement tissue and organs.Biomaterials.2003;24(13):2363-2367. [8]傅刚,杜靖远,杨述华,等.成人成骨细胞骨保护蛋白的表达与年龄关系的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2001,18(6):583-584.[9]郑志永,杨久山,毕荣修,等.人成骨细胞的离体培养和鉴定[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2006,14(4):8-9.[10]苏欣,廖二元,罗湘杭.人成骨细胞体外培养、鉴定及护骨素表达的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2002,8(4):283-287.[11]郝和平,奚延斐.医疗器械监督管理和评价[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2000:66,289-410.[12]王海彬,张兴凯,石印玉,等.人松质骨成骨细胞的培养[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,1999,7(2):1-2.[13]孙海钰,王东,范伟,等.Ⅰ型胶原物理涂层新型多孔硫酸钙支架对兔桡骨缺损修复的影响[J].山西医科大学学报,2008,39(9): 825-829.[14]田学忠,刘越,陈华,等.硫酸钙人工骨研究进展[J].山东医药,2008, 48(9):142-145.[15]Dudas JR,Losee JE, Penascino VM, et al. Leporine-derived adipose precursor cells exhibit in vitro osteogenic potential.J Craniofac Surg. 2008;19(2):360-368.[16]杜明奎,毛克亚,王继芳.β-磷酸三钙与α-半水硫酸钙降解研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2008,29(1):6-25.[17]张梅霞,靳安民,闵少雄,等.仿生型生物玻璃/胶原蛋白/磷脂酰丝氨酸/透明质酸复合支架修复兔桡骨缺损[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2006,10(29):59-62.[18]陈华,陶笙,张伯勋,等.硫酸钙作为骨填充修复材料的新观点与新认识[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(18):180-181.[19]南景天,李鸿,吕国玉,等.多元氨基酸共聚物/含锶硫酸钙复合材料制备及体外降解性能研究[J].动态材料,2010,6(41): 1056-1061.[20]尹飙,苏增贵,杨国忠.组织工程学在骨缺损中的应用研究[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册,1999,22(2):83-87.[21]李文浩,张敏. nHAC膜的体内埋植超徽结构变化[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2004,22(增刊):82-85.[22]郭昭庆,党耕町,王志国.成人成骨细胞培养[J].中华骨科杂志, 1995,15(9):627-630.[23]欧阳钧,王前,王国英,等.人骨膜成骨细胞培养及初步观察[J].中华骨科杂志,1995,15(11):789-790.[24]翦新春,成洪泉,许春姣.天然生物衍生支架材料在骨组织工程中的应用进展[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2003,13(3):239-242.[25]刘刚,胡蕴玉,赵建宁,等.Ⅰ型胶原促进骨髓基质干细胞粘附的细胞机制[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(6):549-552. |

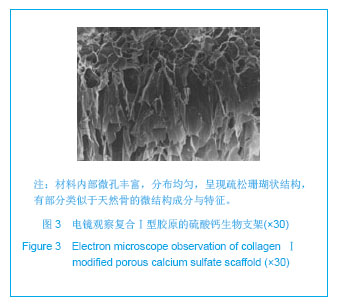


.jpg)
.jpg)